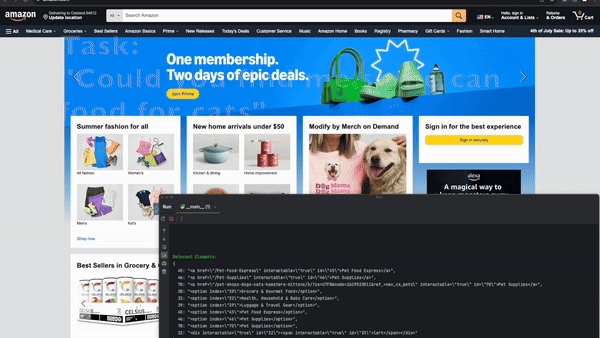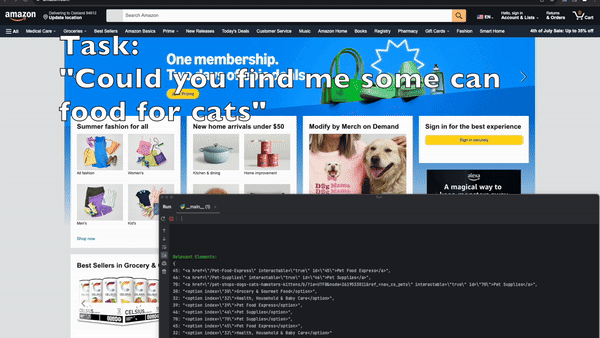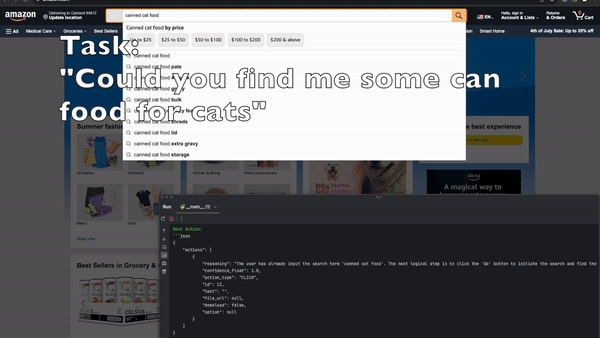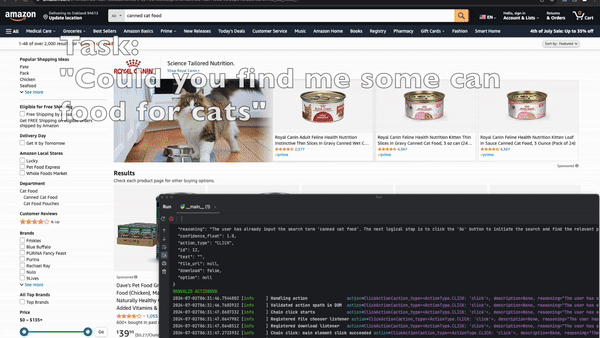
When managing complex tasks, multi-agent systems shine by dividing responsibilities among specialized agents, ensuring each subtask is handled optimally.
Automation of browser-based workflows has traditionally involved writing custom scripts for specific websites, often relying on DOM parsing and XPath-based interactions. These approaches can be fragile and susceptible to breaking when website layouts change. However, a multi-agent approach utilizing LLMs and computer vision adapts to dynamic websites by assigning agents to individual subtasks like element detection, action selection, and monitoring outcomes.
The multi-agent framework enhances:
- Adaptability: Agents handle new websites without customized scripts.
- Resilience: Layout changes don't hinder workflow.
- Scalability: Multiple agents collaborate for a seamless experience across diverse environments.
- Complex Reasoning: Agents leverage LLMs to manage sophisticated interactions.
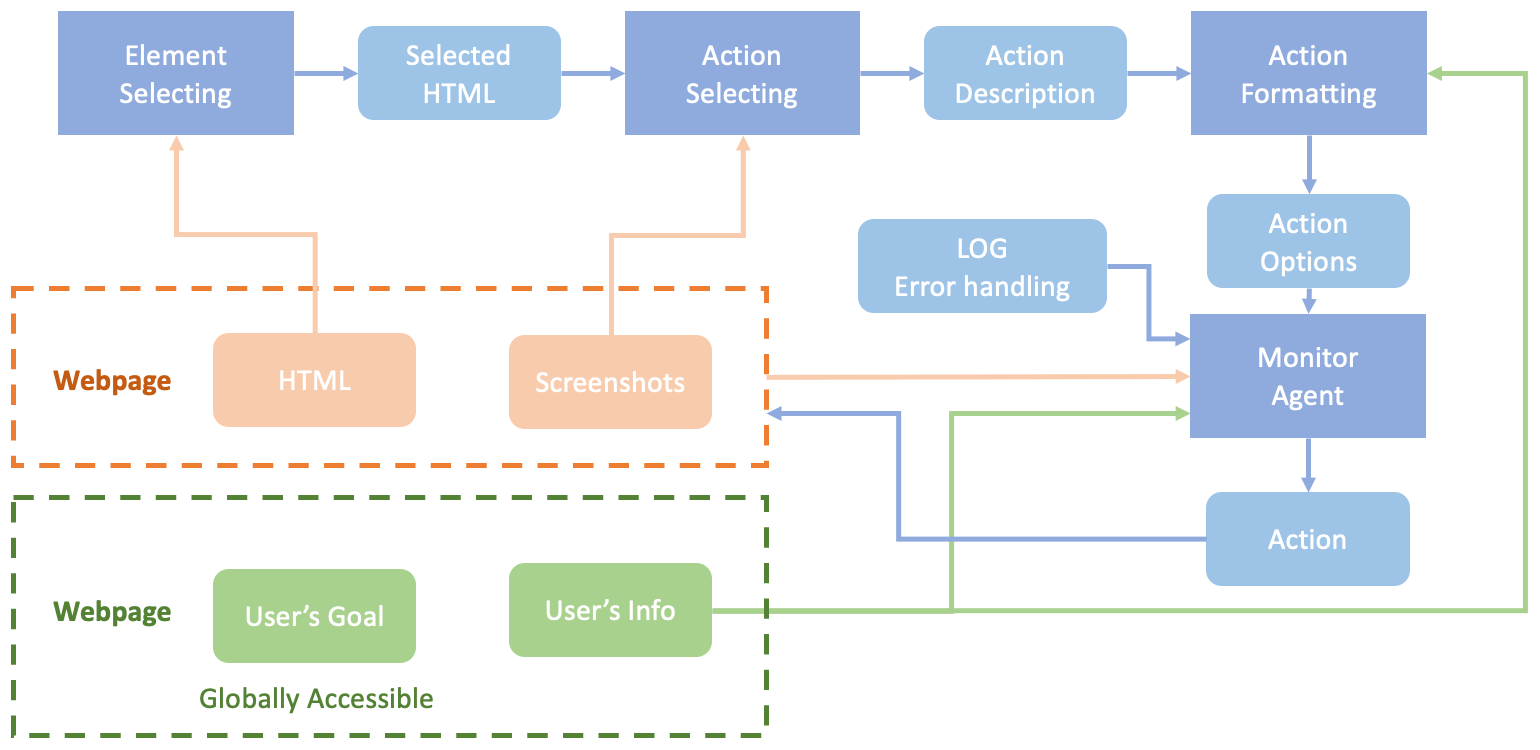
Demonstrations using this multi-agent approach include automated insurance quotes, competitive analysis, and job applications. The system shows high reliability in handling both structured and unstructured interactions. Quantitative tests highlight its accuracy, while developer feedback emphasizes the enhanced automation experience.
Key contributions:
- Introducing a multi-agent architecture for dynamic web environments.
- Performance evaluation across various application domains.
- Feedback integration for future system improvements.
Looking forward, refining the agents' coordination and building robust quality control mechanisms will be crucial in scaling this system for broader use.